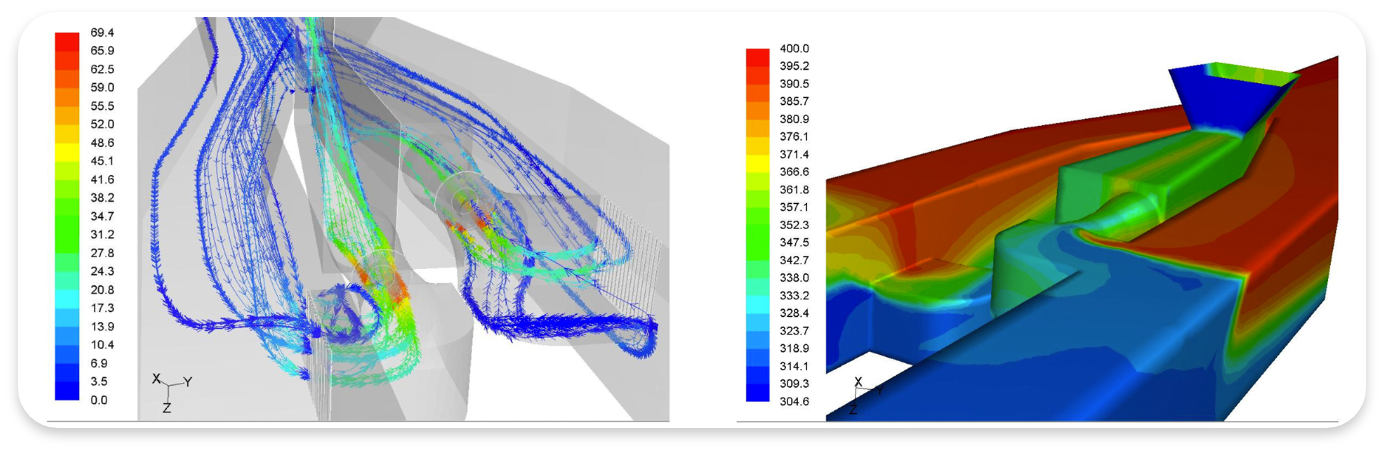
Numerical Study of Turbulent Spray Combustion within the Reverse Flow Combustor of a Turboshaft Engine
Bu çalışma 1000-hp sınıfı bir turboşaft motorunun ters akışlı yanma odasının düzlemselleştirilmiş bir diliminde türbülanslı sprey yanmanın sayısal benzetimini sunmaktadır. Üç girdap vanesi içeren benzetim bölgesi tam halkasal bir yanma odasının bir sektörüne karşılık gelmektedir. Bağlaşık bir Euler-Lagrange yöntemi ile çift fazlı akış, Eddy yitimi kavramı modeli ile de türbülans kimya etkileşimi modellenmiştir. Rastgele yürüyüş modeli ile de sürekli ve dağıtık fazlar arasındaki etkileşim modellenmiştir. Yanma ise tek basamaklı global bir tepkime ile modellenmiş ve tepkime hızı Eddy yitimi kavramı modeli ile sınırlanmıştır. Sonuçlar çıkış düzleminde enjektörlerin tam karşına gelen bölgelerde sıcak noktaların varlığına işaret etmektedir. Benzetim sonuçları bazı seyreltme jetlerinin ana akım içerisine fazla penetre ettiği ve karşı duvara yaklaştığını ifade etmektedir. Bu sonuçlar bir tasarım değişikliğine ihtiyacı ortaya koymaktadır.
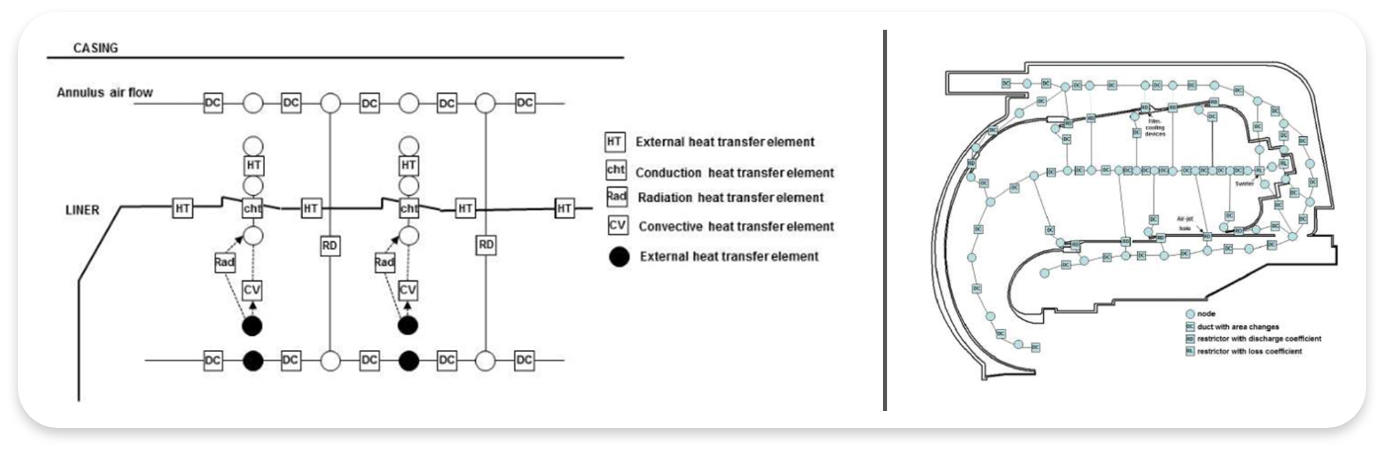
ONE DIMENSIONAL NETWORK MODEL FOR A REVERSE FLOW COMBUSTOR
In this study, a one-dimensional empirical network code was developed for the preliminary design of a reverse flow combustor, which was intended to be used in a 1000 hp turbo-shaft helicopter engine. Network code is able to predict critical design features such as discharge coefficients at each hole set, mass flow rate distributions across the swirler, cooling devices and dilution holes, overall pressure drop across the combustor, liner wall and gas temperatures along the combustor and pollutant emissions at the exit of the combustor. By these means, many design alternatives can be scanned rapidly in early stages of design. Results are presented for a particular combustor geometry operating at idle, cruise and take-o↵ conditions based on the cycle analysis of a turbo-shaft engine design which is intended for light duty helicopter missions. Calculated flow distributions and discharge coefficients were compared with isothermal numerical simulations and reasonably good agreement was achieved for the non-reacting case. On the other hand, liner temperatures for three operating conditions obtained from the network code were examined to see whether the liner temperatures were suitable for liner material and the obtained results showed that this particular design raises doubts when viewed from the predicted high liner temperatures.

ENGINE DESIGN FOR A HALF SCALE MODEL OF JSF UAV WITH HIGH POWER EXTRACTION REQUIREMENTS
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) are the future of air combat. These platforms have generic needs in contrast to manned air platforms. These needs should also be addressed from the engine design perspective. In this study conceptual design for a half-scale UAV (based on the dimensions of the Joint Strike Fighter) is presented. For this purpose a twin spool low by-pass ratio turbofan engine is designed. The main requirement is the high power extraction capability from the engine. This issue is addressed utilizing a novel alternator concept that relies on integrating the stator and the rotor on counter rotating spools. Furthermore on and off design point analyses and component design summaries are also presented. Outcome of the conceptual design task pushes the boundaries of the current state-of-the-art.

QUASI THREE DIMENSIONAL FAN DESIGN FOR A TWIN-SPOOL LOW BYPASS RATIO TURBOFAN ENGINE
Bu çalışmada düşük tali akım (bypass) oranına sahip, çift makaralı bir turbofan motorunun başlangıç tasarımı anlatılmıştır. Tasarıma parametrik çevrim analizinden elde edilen teknik isterlerin özellikleriyle başlanmıştır. Bu bilgiyle teknik özelliklere uygun bir temel motor seçilmiştir. Tasarım süreci fan kademe sayısının diğer kademe parametrelerinin belirlenmesiyle devam etmiştir. Bir sonraki aşama sesaltı koşullarında gerekli sonuçları veren kompresör kanatçık profilinin seçilmesi olmuştur. Profiller pozitif ve negatif tutunma kaybı durumlarından kaçınacak şekilde tasarlanmıştır. Kök profillerin seçiminde uç profillere nazaran düşük lineer hızlarda çalışmasından ötürü kamburluğun bu profillerde büyük olması na dikkat edilmiştir. Radyal yönde profillerin düzenli bir şekilde dizilmesinden dolayı sanki üç boyutlu bir tasarı ma ulaşılmıştır. Son olarak, rotor ve stator kısımlarının katı modeli çizilmiştir.
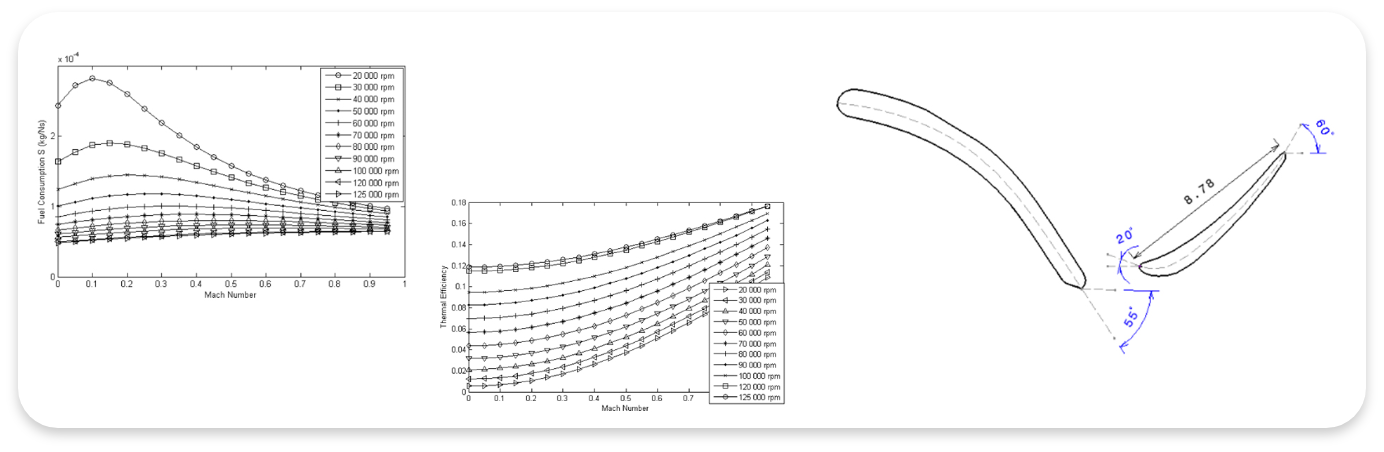
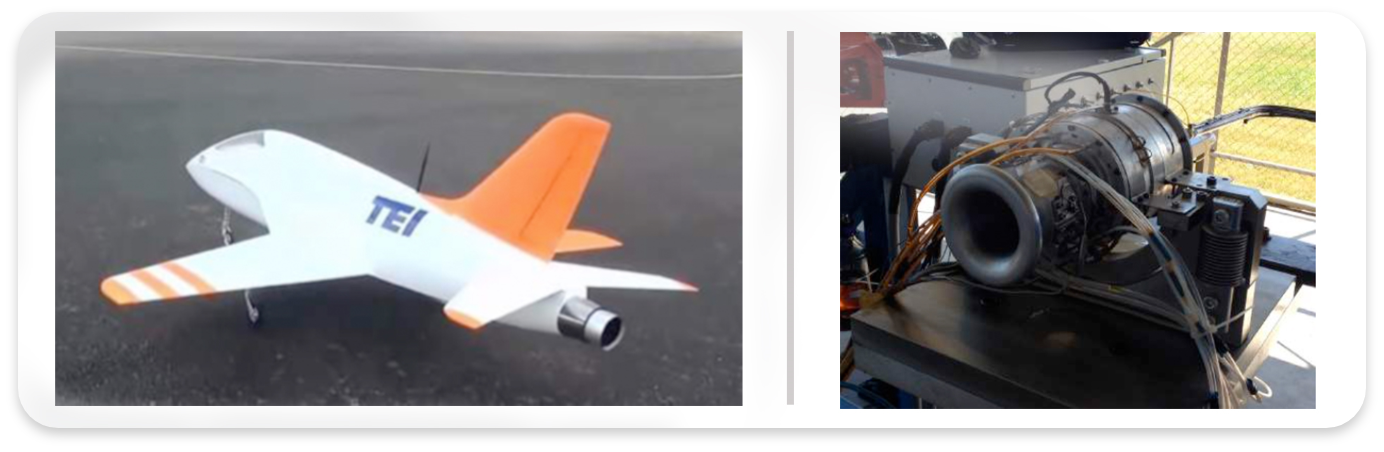
REVERSE ENGINEERING OF A MICRO TURBOJET ENGINE
Reverse engineering is the process of discovering the technological working principles of a device, object or system. This paper in particular, focuses on the reverse engineering of a micro turbojet engine. First, components of gas turbine geometry are scanned and transformed into digitized point cloud format utilizing a three axis scanner. Next, solid geometry of the engine parts were re-constructed in computer aided drafting environment from these data. Furthermore, performance maps of individual components are either calculated or certain assumptions were made as to their behavior. On and off design point engine performance has been determined through a parametric cycle analysis. Obtained results are in line with the reported performance parameters of the reverse engineered engine. This study demonstrates the use of reverse engineering procedures, when designing from scratch would not be as practical. This approach can cut down the overall turnover time for a new design.

150 mm ŞOK GENİŞLEME TÜPÜ TEST DÜZENEĞİNİN KAVRAMSAL VE MEKANİK TASARIMI
Ses üstü ve hipersonik akış testlerinin kısa sürede yapılabileceği bir şok- genişleme tüpü test düzeneğinin ideal gaz varsayımı altında kavramsal tasarımı gerçekleştirilmiştir. Bu hesaplamalara ve dünyadaki benzer örneklere dayanarak 7.3 MJ/kghava durma noktası entalpisine ulaşabilecek 150 mm anma çaplı bir şok-genişleme tüpünün mekanik tasarımı yapılmıştır. Sistem darbe esasına göre çalıştığı için tipik test süreleri 150 ila 1000 mikrosaniye mertebesindedir. Test süresini maksimize etmek için kesimlerin boyu modüler bir şekilde ayarlanabilmektedir.İstenilen test koşulları ilk doldurma basınçlarının ayarlanması ile değiştirilebilmekte ve böylece değişik Mach sayılarında testler yapabilmek için lüle değiştirmek gerekmemektedir. Bu test düzeneği kullanarak birçok yüksek entalpili akışın deneysel incelemesini yapmak mümkün olabilecektir. Söz konusu test düzeneğinin kurulumu, TÜBİTAK-SAGE bünyesinde yürütülmekte olan İç Balistik Tasarım Altyapısı (İBTA) Projesi kapsamında Lalahan yerleşkesinde gerçekleştirilecektir.

OPTIMIZATION OF A CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR IMPELLER UTILIZING GENETIC ALGORITHM COUPLED WITH ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORKS
Impeller geometry optimization is performed using genetic algorithms coupled with artificial neural networks. Impeller geometry is parameterized using Bezier splines. Hub and shroud profiles are generated first using Bezier curves. Thereafter blade cross-sections, which are parametrically generated by defining camberline, thickness distribution and meridional profile, are lofted along the quasi-diagonal direction. Steady state RANS CFD simulations are performed for a family of parameters that are picked according to design of experiments rule. These CFD results are used to train the ANN. Genetic algorithm uses the output of the ANN in order to optimize the input parameters that define the centrifugal compressor impeller. Optimized impeller outperforms the baseline by 5% in terms of isentropic efficiency at the operating point.
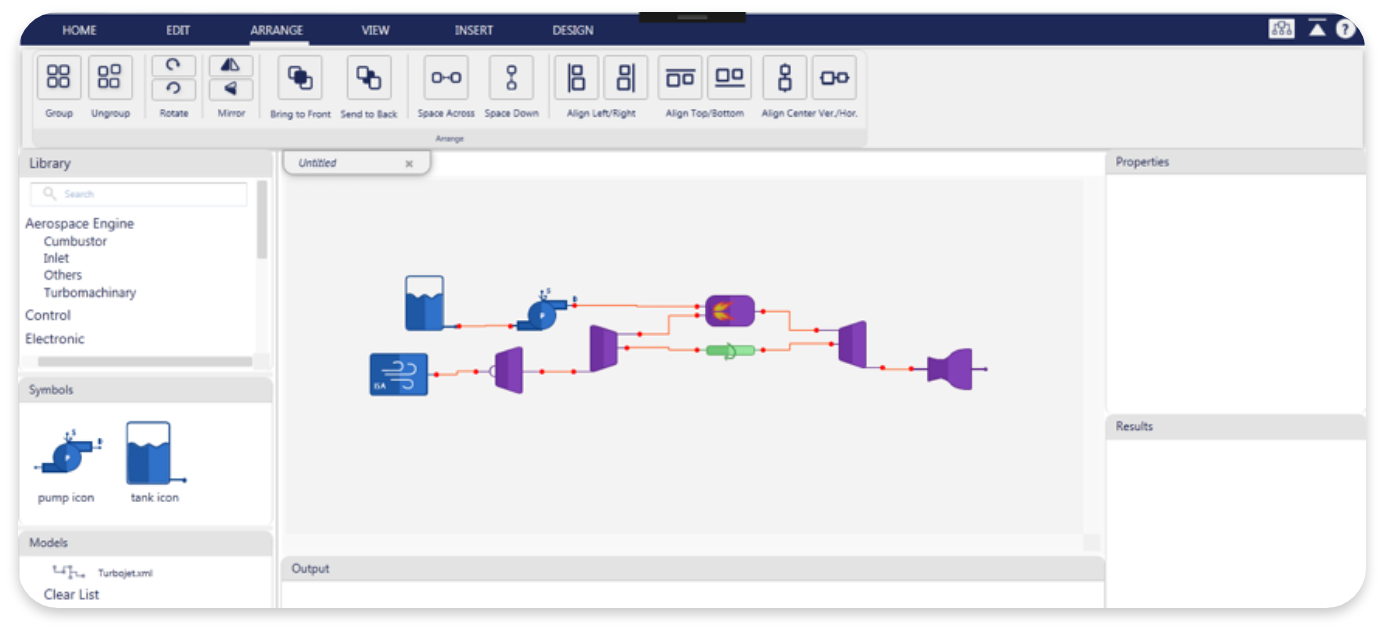
A Model-Based Design Software for Propulsion System Design
We have developed a rapid prototype for the core layer, one that handles computations, under MATLAB environment. This core at the time being is able to solve the steady-state behavior of simple pipe networks and some turbo-machinery components. We also developed a user friendly graphical user interface (GUI) and started porting our MATLAB code into C#. Now, we can show a stand-alone proof-of-concept desktop application demo that can solve pipe networks that are defined by the user via drag and drop interactions. We also began implementing databases for some standard components. As a next step we will start implementing Git integration which lets teams of all sizes to collaborate easily in a shared project.
TERMAL HİDROLİK SİSTEMLERİN DİJİTAL İKİZLERİNİN OLUŞTURULMASI İÇİN NESNE YÖNELİMLİ BİR YAZILIM GELİŞTİRİLMESİ
Termal hidrolik sistemlerin bilgisayar ortamında dijital ikizlerinin oluşturulması için FlowNetMaster ismi ile yeni bir yazılım geliştirilmiştir. FlowNetMaster tamamen nesne yönelimli programlama paradigmaları ile C# dilinde .NET Framework teknolojisi ile model-gösterim-gösterim modeli (MVVM) mimari yapısı kullanılarak geliştirilmiştir. İçerdiği veritabanı sayesinde standart komponentler (borular, pompalar, fitting elemanları) kullanıcı tarafından kolayca seçilebilmekte ve istenildiğinde kullanıcı tarafından yeni komponentler tanımlanabilmektedir. Modelin oluşturulması için kullanıcı kütüphanelerden seçtiği komponentleri (örneğin ısı değiştiricisi, boru v.b.) sürükle bırak etkileşimlerle çizim tuvaline yerleştirmekte daha sonra ise bu ortamda komponentlerin birbirlerine bağlantılarını yapmaktadır. Yazılım bu modeli çekirdek katmanında (model katmanı) bir diferansiyel cebirsel denklem takımına dönüştürmekte ve modelin sürekli ve geçici rejimlerdeki davranışını çözebilmektedir. Yazılımın standart termo-fiziksel kütüphanesinde yüzden fazla akışkan (su, hava, soğutma gazları ve sıvıları, nemli hava, antifriz çözeltileri v.s.) tanımlıdır. Ayrıca kullanıcıya da kendi istediği akışkanı tanımlayabilme özelliği sunulnuştur. Yazılımın sahip olduğu gösterge paneli (insan makine arayüzü) özelliği sayesinde kullanıcılar model ile etkileşebilmekte ve model çalışırken göstergeleri takip edebilmektedirler.
